【论文阅读】MIMICS: A Large-Scale Data Collection for Search Clarification
文章目录
- Motivation
- Intro
- Contribution
- MIMICS-Click
- MIMICS-ClickExplore
- MIMICS-Manual
- Data Analysis
- Question Template Analysis
- Analyzing Engagement Based on Clarification Impression
- Analysis Based on Query Length
- Analysis Based on the Number of Candidate Answers
- Analyzing Click Entropy Distribution on Candidate Answers(confused)
原文链接: MIMICS: A Large-Scale Data Collection for Search Clarification (arxiv.org)
Motivation
The research community still feels the lack of a large-scale data for studying different aspects of search clarification.
Intro
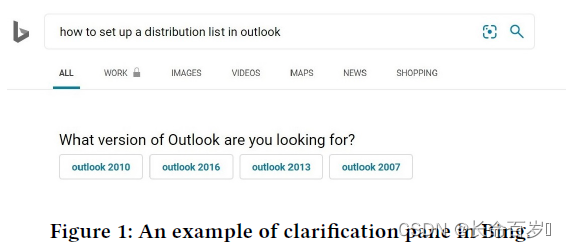
- each clarification in MIMICS consist of a clarifying question and up to five candidate answers
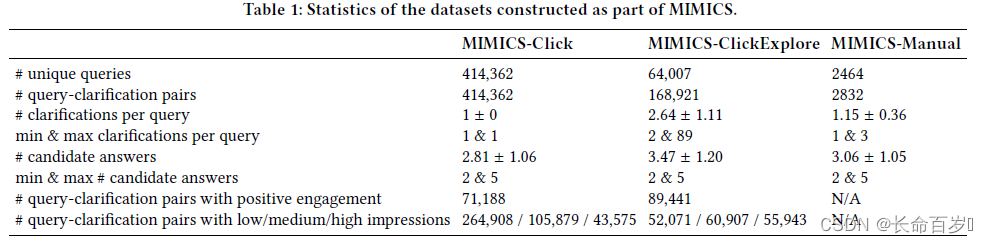
All the datasets presented in this paper only demonstrate the queries from the en-US market.
MIMICS-Click and MIMICS-ClickExplore are based on user interaction in Bing.
MIMICS-Manual is based on manual annotations of clarification paned by multiple trained annotators.
Contribution
Create MIMICS, consists of three datasets:
MIMICS-Click: includes over 400k unique queries with the associated clarification panes.MIMICS-ClickExplore: is an exploration data and contains multiple clarification panes per query. It includes over 60k unique queries.MIMICS-Manual: is a smaller dataset with manual annotations for clarifying questions, candidate answer sets, and the landing result page after clicking on individual candidate answers.
MIMICS-Click
-
only kept the queries for which a clarification pane was rendered in the search engine result page (SERP).
-
the clarification panes were solely generated based on the submitted queries, therefore they do not include session and personalized information
-
This resulted in 414,362 unique queries, each associated with exactly one clarification pane. Out of which 71,188 of clarifications have received positive clickthrough rates.
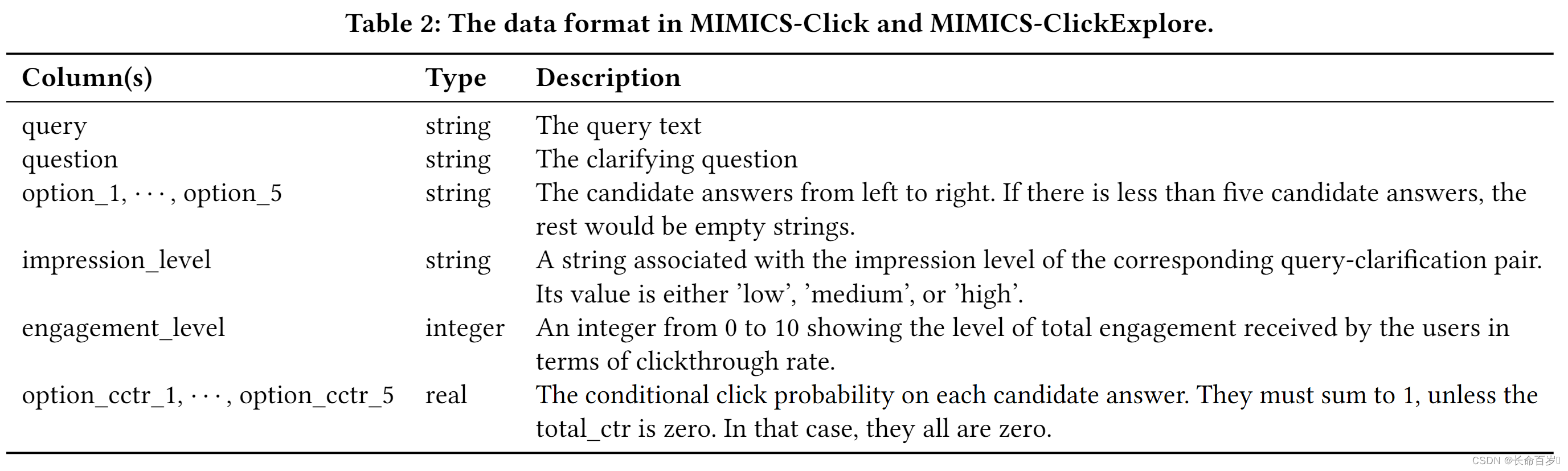
MIMICS-ClickExplore
Although MIMICS-Click is a invaluable resource for learning to generate clarification and related research problems, it does not allow researchers to study some tasks, such as studying click bias in user interactions with clarification.
-
we used the top-m clarifications generated by our algorithms and presented them to different sets of users. The user interactions with multiple clarification panes for the same query at the same time period enable
comparison of these clarification panes -
The resulted dataset contains 64,007 unique queries and 168,921 query-clarification pairs. Out of which, 89,441 query-clarification pairs received positive engagements.
-
Note that the sampling strategies for MIMICS-Click and MIMICS-ClickExplore are different which resulted in significantly more query-clarification pairs with low impressions in MIMICS-Click.
MIMICS-Manual
Click does not necessarily reflect all quality aspects. In addition, it can be biased for many reasons.
- we randomly sampled queries from the query logs to collect manual annotations for a set of realistic user queries.
- further used the same algorithm to generate one or more clarification pairs for each query
- Each query-clarification pair was assigned to at least three annotators
step1: asked the annotators to skim and review a few pages of the search results returned by Bing
step2: Each clarifying question is given a label 2 (Good), 1 (Fair), or 0 (Bad)(does not show the candidate answers to the annotators at this stage)
step3: the annotators were asked to judge the overall quality of the candidate answer set(2, 1, 0)
step4: Annotating the Landing SERP(the SERP after clicking one answer) Quality for Each Individual Candidate Answer
- Our annotations resulted in over 2.4k unique queries and over 2.8k query-clarification pairs
Note: in case of having a generic template instead of clarifying questions (i.e., “select one to refine your search”), we do not ask the annotators to provide a question quality labels.
Data Analysis
Question Template Analysis
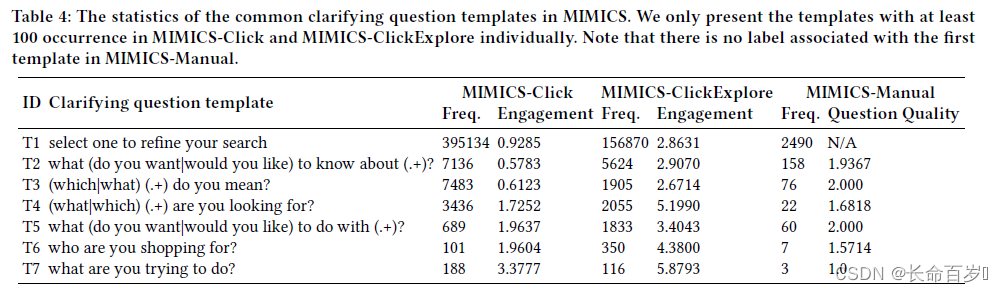
- the last four templates (T4 - T7)(less frequent in the dataset and more specific) have led to higher engagements compared to T1, T2, and T3 in both MIMICS-Click and MIMICS-ClickExplore
- the exploration dataset has higher average engagements compared to MIMICS-Click.
- The reason is that the number of query-clarification pairs with zero engagements in MIMICS-Click are higher than those in MIMICS-ClickExplore
Analyzing Engagement Based on Clarification Impression
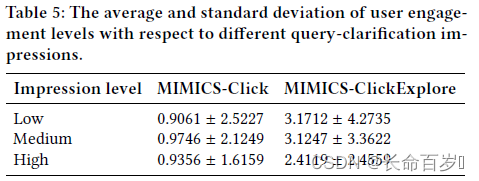
MIMICS-Click and MIMICS-ClickExplore contain a three-level impression label per query-clarification pair
- there is negligible difference between the average engagements across impression levels
Analysis Based on Query Length
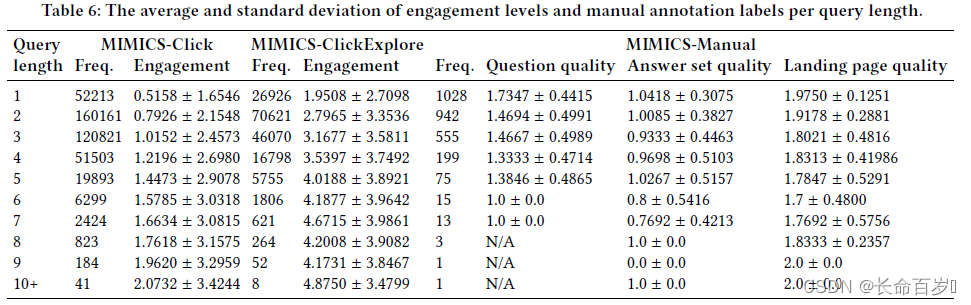
We study user engagements and manual quality labels with respect to query length
-
the average engagement increases as the queries get longer.
- longer queries are often natural language questions, while short queries are keyword queries
-
this is inconsistent with the manual annotations suggesting that single word queries have higher question quality, answer set quality, and also landing page quality
- This observation suggests that user engagement with clarification is not necessarily aligned with the clarification quality
Analysis Based on the Number of Candidate Answers
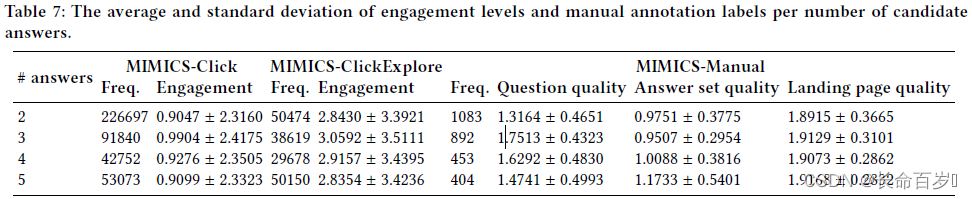
- there is a small difference between average engagements in both
MIMICS-ClickandMIMICS-ClickExploredatasets- The clarifications with three candidate answers have led to a slightly higher engagement than the rest.
- The clarifications with three candidate answers has best question quality but worst answer set quality
- This highlights that the question quality may play a key role in increasing user engagements
Analyzing Click Entropy Distribution on Candidate Answers(confused)
MIMICS-Click and MIMICS-ClickExplore both contain conditional click probability on each individual answer.
The entropy of this probabilistic distribution demonstrates how clicks are distributed across candidate answers.
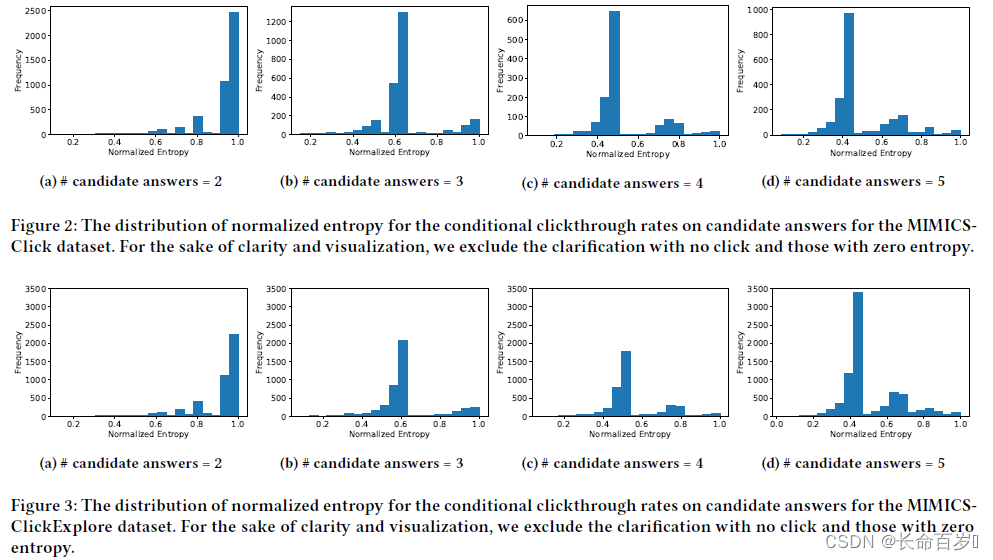
- the number of peaks in the entropy distribution is aligned with the number of candidate answers.
- The entropy values where the histogram peaks suggest that in many cases there is a uniform-like distribution for m out of n candidate answers
