@Resource和@Autowired 区别和源码详解
一、前言
我们知道在Spring注入Bean对象的时候,可以在成员变量上写@Resource和@Autowired两种,那么他们的区别是什么呢?
结论:
@Resource 按照Bean对象的名称去查找,并判断Spring工厂中的Bean对象类型与要注入的成员变量的类型是否匹配。如果按名称找不到,则按照类型去匹配。
@Autowired 按照Bean对象的类型去匹配。
二、源码分析
首先要知道什么时候时候去注入,就是在执行AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类创建Bean方法的时候,doCreateBean方法中的populateBean中
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)throws BeanCreationException {// Instantiate the bean.BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;if (mbd.isSingleton()) {instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);}..................// Initialize the bean instance.Object exposedObject = bean;try {populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);}}populateBean中的 ibp.postProcessProperties()方法
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {...........................PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;if (hasInstAwareBpps) {if (pvs == null) {pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();}for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);if (pvsToUse == null) {if (filteredPds == null) {filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);}pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);if (pvsToUse == null) {return;}}pvs = pvsToUse;}}}if (needsDepCheck) {if (filteredPds == null) {filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);}checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);}if (pvs != null) {applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);}}ibp.postProcessProperties()方法有很多实现类,其中处理@Resource的在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中。
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);try {metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of resource dependencies failed", ex);}return pvs;}private InjectionMetadata findResourceMetadata(String beanName, final Class clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {if (metadata != null) {metadata.clear(pvs);}metadata = buildResourceMetadata(clazz);this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);}}}return metadata;}在buildResourceMetadata方法里
private InjectionMetadata buildResourceMetadata(final Class clazz) {List elements = new ArrayList<>();Class targetClass = clazz;do {final List currElements = new ArrayList<>();ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {if (webServiceRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static fields");}currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(field, field, null));}else if (ejbRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(ejbRefClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static fields");}currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(field, field, null));}else if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static fields");}if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(field.getType().getName())) {currElements.add(new ResourceElement(field, field, null));}}});ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {return;}if (method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {if (webServiceRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static methods");}if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);}PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));}else if (ejbRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(ejbRefClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static methods");}if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);}PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));}else if (bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static methods");}Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();if (paramTypes.length != 1) {throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);}if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(paramTypes[0].getName())) {PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);currElements.add(new ResourceElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));}}}});elements.addAll(0, currElements);targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();}while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);} 会循环判断类中的Field和Method,找到上面有Resource注解的属性。之后创建ResourceElement节点 并add到currElements的List中等待处理。ResourceElement类初始化。
public ResourceElement(Member member, AnnotatedElement ae, @Nullable PropertyDescriptor pd) {super(member, pd);Resource resource = ae.getAnnotation(Resource.class);String resourceName = resource.name();Class resourceType = resource.type();// ** 1 **this.isDefaultName = !StringUtils.hasLength(resourceName);if (this.isDefaultName) {resourceName = this.member.getName();if (this.member instanceof Method && resourceName.startsWith("set") && resourceName.length() > 3) {resourceName = Introspector.decapitalize(resourceName.substring(3));}}else if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {resourceName = embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(resourceName);}// ** 2 **if (Object.class != resourceType) {checkResourceType(resourceType);}else {// No resource type specified... check field/method.resourceType = getResourceType();}this.name = (resourceName != null ? resourceName : "");this.lookupType = resourceType;String lookupValue = resource.lookup();this.mappedName = (StringUtils.hasLength(lookupValue) ? lookupValue : resource.mappedName());Lazy lazy = ae.getAnnotation(Lazy.class);this.lazyLookup = (lazy != null && lazy.value());}ResourceElement节点初始化时,在1处,先判断@Resource的name是否为空,如果为空则使用Field的默认名字。
@Component
public class BeanA {@Resource(type = BeanC.class)private BeanFather beanB;
}在2处,判断@Resource注解标识的type类型与定义类型的是否一致。如示例,判断BeanC是否属于BeanFather类型。
之后进入postProcessProperties的metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);方法。在InjectionMetadata类的inject方法
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {Collection checkedElements = this.checkedElements;Collection elementsToIterate =(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);}element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);}}}protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)throws Throwable {if (this.isField) {Field field = (Field) this.member;ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));}else {if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {return;}try {Method method = (Method) this.member;ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));}catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {throw ex.getTargetException();}}} 判断是节点是Field或是Method。进入getResourceToInject方法,回到CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类的ResourceElement内部类的getResourceToInject方法
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {return (this.lazyLookup ? buildLazyResourceProxy(this, requestingBeanName) :getResource(this, requestingBeanName));}进入getResource方法。
protected Object getResource(LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {if (StringUtils.hasLength(element.mappedName)) {return this.jndiFactory.getBean(element.mappedName, element.lookupType);}if (this.alwaysUseJndiLookup) {return this.jndiFactory.getBean(element.name, element.lookupType);}if (this.resourceFactory == null) {throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.lookupType,"No resource factory configured - specify the 'resourceFactory' property");}return autowireResource(this.resourceFactory, element, requestingBeanName);}protected Object autowireResource(BeanFactory factory, LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {Object resource;Set autowiredBeanNames;String name = element.name;if (factory instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory) {AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = (AutowireCapableBeanFactory) factory;DependencyDescriptor descriptor = element.getDependencyDescriptor();// ** 1 **if (this.fallbackToDefaultTypeMatch && element.isDefaultName && !factory.containsBean(name)) {autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();resource = beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);if (resource == null) {throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.getLookupType(), "No resolvable resource object");}}else {// ** 2 **resource = beanFactory.resolveBeanByName(name, descriptor);autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);}}else {resource = factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);}if (factory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) factory;for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {if (requestingBeanName != null && beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {beanFactory.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, requestingBeanName);}}}return resource;} 两种情况:
(1):autowireResource方法在1处,会根据定义判断是否使用默认名字,以及BeanFactory中是否含有这个名字的Bean,如果不含这个name的bean,则调用beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);方法。
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,@Nullable Set autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);}else if (ObjectFactory.class == descriptor.getDependencyType() ||ObjectProvider.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);}else if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return new Jsr330Factory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);}else {Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(descriptor, requestingBeanName);if (result == null) {result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);}return result;}} 通过doResolveDependency方法
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,@Nullable Set autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {.....................Class type = descriptor.getDependencyType();......................Map matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {if (isRequired(descriptor)) {raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);}return null;}String autowiredBeanName;Object instanceCandidate;if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);if (autowiredBeanName == null) {if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);}else {// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).return null;}}instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);}..................} 该方法通过 findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);去查找。因为根据beanName已经不存在了,所以主要是根据type,如果找到两个相同类型的Bean,又没有标识@Primary或优先级,则报错(在if (matchingBeans.size() > 1)中判断)。
(2):autowireResource方法在1处,会根据定义判断是否使用默认名字,以及BeanFactory中是否含有这个名字的Bean,如果包含这个name的bean,则调用 beanFactory.resolveBeanByName(name, descriptor); 在 // ** 2 ** 处
public Object resolveBeanByName(String name, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);try {return getBean(name, descriptor.getDependencyType());}finally {ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);}}public T getBean(String name, Class requiredType) throws BeansException {return doGetBean(name, requiredType, null, false);} 该方法会根据name找到bean,并判断bean的类型,和@Resource定义的是否一样。在doGetBean中最后一段判断。如下代码:
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {try {T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);if (convertedBean == null) {throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());}return convertedBean;}catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);}throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());}}这里可能有人会问,在生成@Resource注解的ResourceElement初始化时,不是已经判断了@Resource的type和Field的类型是否一致了吗。其实主要是为了解决注入接口类型的Bean对象问题。
比如我有BeanB和BeanC两个类,都实现了BeanFather这个接口,那么在BeanA中,如果我这样写
@Component
public class BeanA {@Resource(type = BeanC.class)private BeanFather beanB;
}在生成ResourceElement时,BeanC确实属于BeanFather,但是到doGetBean实际注入中,因为在BeanFactory中有BeanB这个对象,通过@Resource获取时优先根据名字,那么获取到的BeanB这个类型就和要注入的BeanC不符合了,就会抛错,因为BeanB和BeanC并不能互相转换。
报错如图
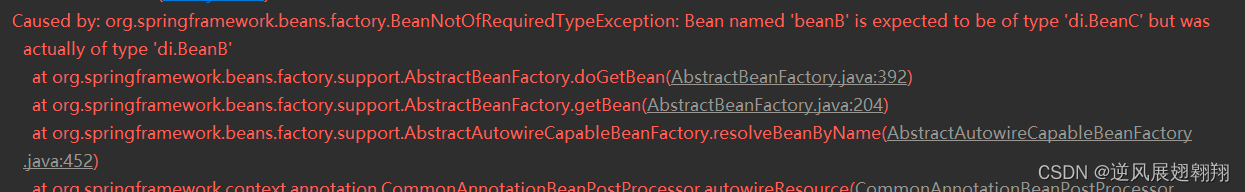
@Resource就分析完了,@Autowired的处理类是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。内容基本类似,也是在postProcessProperties中,生成的节点是AutowiredFieldElement。在InjectionMetadata类的inject方法时
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {Field field = (Field) this.member;Object value;if (this.cached) {value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);}else {DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());Set autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();try {value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);}catch (BeansException ex) {throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);}synchronized (this) {if (!this.cached) {if (value != null || this.required) {this.cachedFieldValue = desc;registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());}}}else {this.cachedFieldValue = null;}this.cached = true;}}}if (value != null) {ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);field.set(bean, value);}}} 直接执行的value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);和@Resource的beanFactory中不包含name执行的一样,根据类型注入。
三、总结
@Resource 按照Bean对象的名称去查找,并判断Spring工厂中的Bean对象类型与要注入的成员变量的类型是否匹配。如果按名称找不到,则按照类型去匹配。
@Autowired 按照Bean对象的类型去匹配。
